Pole-mounted transformers are very important components of the power grid network that facilitate efficient voltage regulation and protect the distribution of power to residential, commercial, and industrial areas. Two common types of these transformers are single-phase and three-phase pole-mounted transformers. The purpose of each transformer is different and on different principles for different applications.
What are the differences between single-phase and three-phase pole-mounted transformers?
Basic Design and Construction
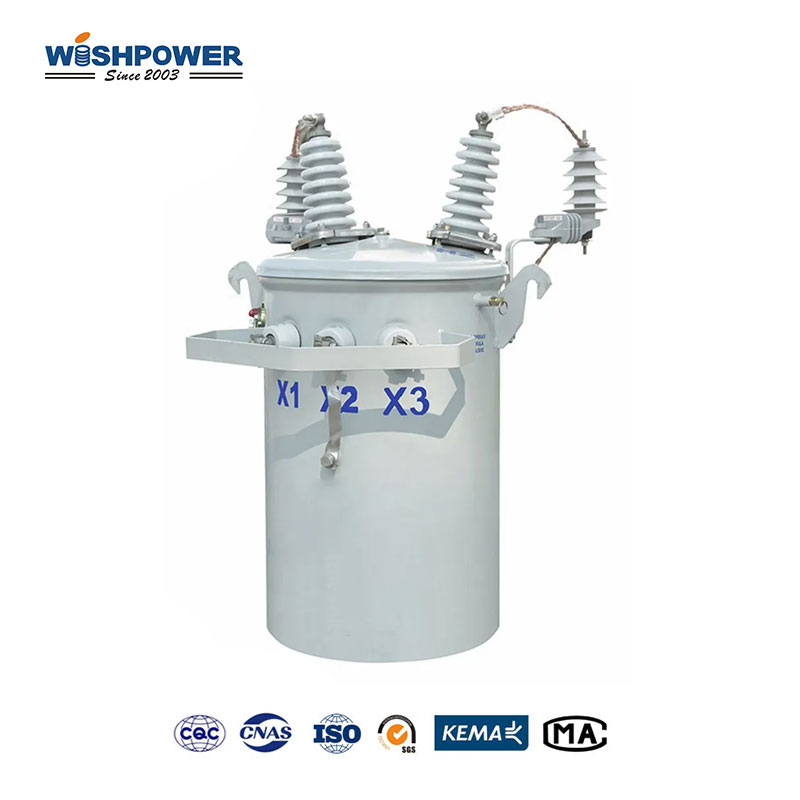
Single-phase Transformer: Membrane-bonded transformers are simpler devices, having only one winding on the primary and the secondary sides. The single-phase alternating current (AC) sine wave used in these transformers follows it. Their load requirements are relatively modest and they are designed for low power applications.
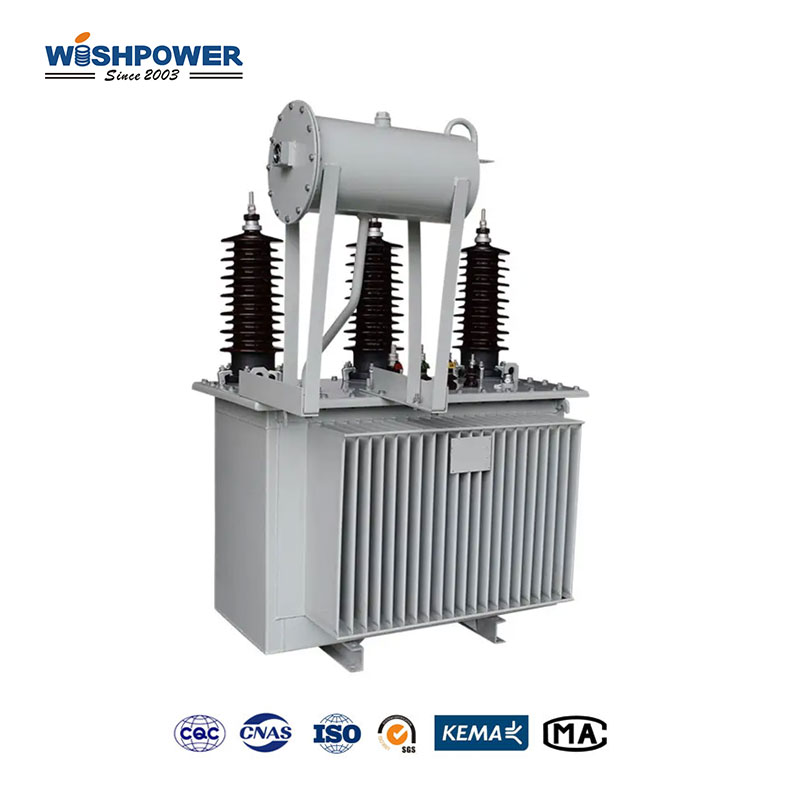
Three-phase Transformer: On the other hand, more complex are three-phase pole-mounted transformers. The primary side and the secondary side windings have three with one of three phases of the AC supply connected to each of the three windings. Industrial and commercial sectors rely on these transformers because higher power demand needs the efficiency and stability these transformers offer in a three-phase system.
Power Capacity and Load Distribution
Single-Phase Transformers: Thus, single-phase transformers are preferred due to their simpler design, although the power capacity is lower. Occasionally, they’re used to move power to individual homes or even little structures. In large-scale applications, they are less efficient at load distribution because they cannot handle a great amount of power.
Three-Phase Transformers: High power capacity and efficient load distribution design make three-phase transformers. Usually used to transmit a major amount of electricity or power to factories, large buildings, or local utility grids, they can handle large loads. The three-phase format gives greater smoothness to power delivery and has less ripple on the voltages, making them perfect for heavy-duty and industrial processes.
Voltage Regulation and Efficiency
Single-Phase Transformers: Simple voltage regulation but not the best efficiency for long-distance transmission, single-phase transformers exist. This is because there is no continuous power flow between phases so voltage drops are much more common. This type of limitation makes them suitable for short-distance power distribution.
Three-Phase Transformers: Long-distance transmission is better served by three-phase designs which have better voltage regulation and higher efficiency. It delivers power over three separate phases and keeps voltage more stable as well as minimizing energy losses. However, this advantage makes them a preferred choice for regional and national power grids.
Installation and Maintenance
Single-Phase Transformer: Installation of single-phase pole-mounted transformers is simpler and less cost-effective as they have a smaller size and simple design. They are an economical choice for low-load areas with minimal maintenance requirements.
Three-Phase Transformer: The three-phase transformers are more complex to install because of their larger size and synchronization of three separate windings. This increases the maintenance requirements, and the system needs technicians trained in maintaining all three phases, as well as regular inspections to make sure all three phases are indeed up and running. However, the maintenance costs are usually much higher, but their durability and efficiency usually outperform.
Applications
Single-Phase Transformer: The transformers are found in rural suburban areas, supplying power to individual homes, farms, and small businesses. They are also used for small lighting systems and appliances needing less energy.
Three-Phase Transformers: In urban areas, three-phase transformers are used to power industrial plants, shopping malls, large office buildings, and so on. Heavy industries manufacturing and mining need stable, high power and they are also useful.
Cost Impact
Single-Phase Transformer: Single-phase transformers have smaller sizes and are of simpler construction therefore they are cheaper initially. They are therefore attractive for low-power usage areas. However, they are limited in capacity and may need many units to cover a broader land area, thus raising total expenses.
Three-Phase Transformers: Three-phase transformers are more expensive up front, but because of can handle larger loads and distribute power more efficiently, these run at a lower operating cost over time. Due to their long-term economic benefits, they make better choices for large-scale applications.
Energy Efficiency
Single-Phase Transformers: Compared to three-phase transformers, the efficiency of these transformers at high-power applications is less. Wasted energy can have a bigger impact on our environment when we use single-phase systems.
Three-Phase Transformers: However, inherently three three-phase transformers are much more energy efficient than single-phase transformers by a much more important measure, which is the reduction in energy losses during transmission and distribution. Using this efficiency aids low carbon footprints, accomplishing contemporary energy conservation goals, and being more environmentally friendly.
Durability and Operational Stability
Single-Phase Transformers: Single-phase transformers are relatively durable but may have difficulty maintaining operational stability during fluctuating loads or high-demand situations. sudden changes in power demand limit their reliability in a dynamic environment, their performance can be affected.
Three-Phase Transformers: Excellent durability and operational stability for three-phase transformers is obtained from the robust design. Being highly reliable in critical applications continuous power delivery over three phases minimizes interruptions.
Conclusion
Single-phase and three-phase pole-mounted transformers have similarly important roles in the power distribution process but their differing characteristics qualify them for different situations. A single-phase transformer is low low-power, localized application that is simple, and less cost effective. On the other hand, transformers used on large-scale, high-power systems rely on efficiency, reliability, and stability and do not compare favorably with three-phase transformers. With this understanding, utility providers and engineers know which transformer to choose that takes into account some specific operational and environmental requirements so that the distribution network would run optimally and efficiently.
If you have different opinions or want to know more, please leave a message on the website or contact us directly at info@wishpower.net

















